Fiori and HANA DB
1.
What is different type of deployment model? - Hub vs Embedded
HUB:
Developers can make changes to the UI without worrying about the back-end development authorizations.
A single point of access is provided to multiple back-end systems;
it supports the composition and routing of multiple back-end systems, as well.
Because there’s no direct access to the back-end data, you can benefit from enhanced security.
The lifecycle of UI applications can be decoupled from the back-end.
Production scenarios with medium to high loads are supported.
The only disadvantage of this kind of deployment is that it needs an additional server for SAP Gateway.
Embedded:
The advantages of using an embedded deployment include the following:
No additional system for SAP Gateway is required.
Direct access is provided to the business data and business logic.
Only one remote call to the SAP system is necessary.
Disadvantages of using this deployment option include the following:
Production use is only suitable for low-load production systems not for medium to high loads.
SAP Gateway must be configured on every system when multiple SAP Business Suite systems are used.
Components can only be upgraded during system maintenance;
2.
Types of Tile/Apps in Fiori?
Transactional(Tcode based) vs Analytic(provide business insight using complex algo(Sales order fulfillment)) vs Navigation (itself an app navigated to/from another app)
3.
What is Tile, groups and catalogue (Technical and business) ?
Tile is container that represents an app on Fiori launchpad, so its used to display and launch App
A catalog is a set of Tiles / Applications you want to make available for one role.
Technical catalog act as a repository of tiles and target mappings.
Business catalog contain references to the tiles and target mappings defined in technical Catalogs.
A G
roup is a subset of Applications from one or more catalogs
4.
T-code to activate services in Fiori? /N/IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE
5. What is Target Mapping?
you map a navigation target to the combination of a semantic object and an action, also known as an intent.
6. A
semantic object represents a business entity such as a customer, a sales order, or a product, supplier. Using semantic objects, you can bundle applications that reflect a specific scenario.
7
Mandatory Basic services to load Fiori Launchpad?
Page Builder, Interop, Easy Access Menu and User Menu
8.
What is OData services? front end and backend name? - IWSG (front) & IWSV(back)
OData is a resource-based web protocol for querying and updating data.
9.
What are diff type of role in HANA? -
Design time(Repository) and Run time(Catalog role)
10.
Diff type of HANA privileges?
11.
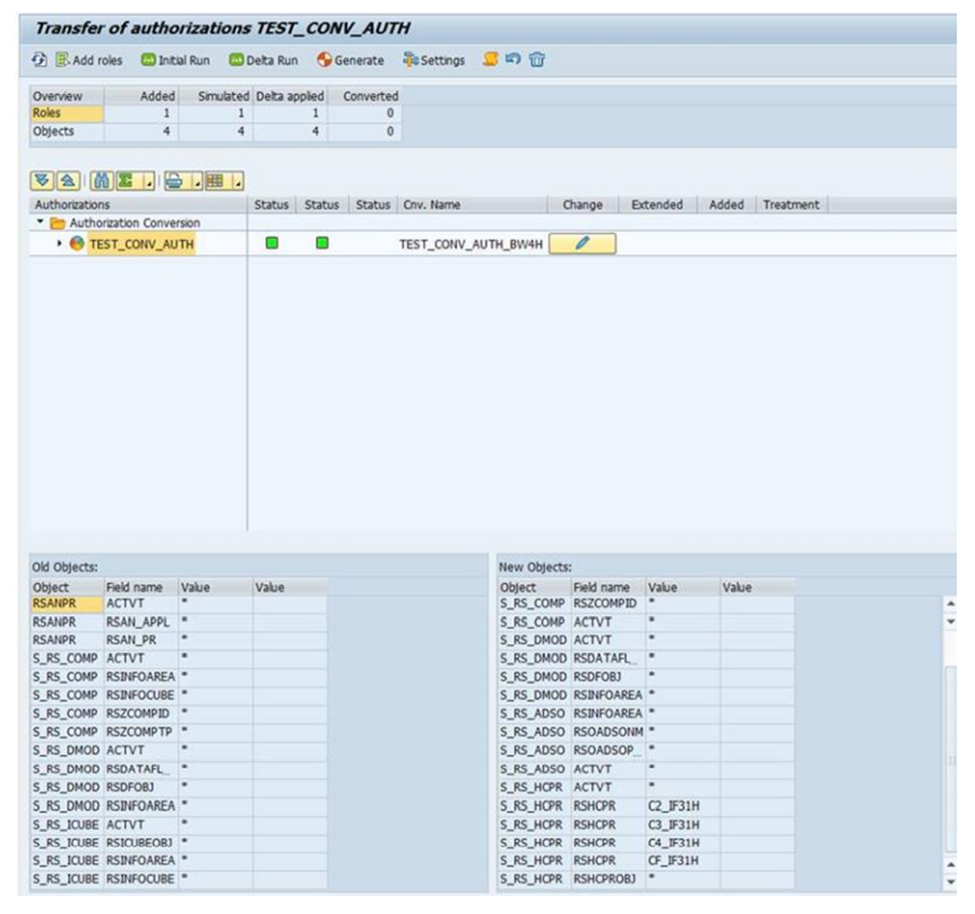
What is diff BW on HANA and Bw4HANA?
12.
Why has SAP provided Spaces and Pages concept over Group and Catalogue?
13. What is the main advantage of using Spaces and Pages in Fiori? BI Security -1.
What is different level of access in hierarchy type characteristics?
2.
Table for analysis auth?
3.
What is Colon (:) and Hash (#) in AA?
4.
Diff Auth object to execute query in BW? - S_RS_COMP, S_RA_COMP1, A_RS_FOLD
5.
Auth Object to Restrict Query access? S_RS_AUTH
6.
step by step BI security? - https://blogs.sap.com/2009/02/26/step-by-step-sap-bi-security
ECC Security-1.
What is diff between su24 and su25?
2.
Steps of su25?
3.
Custom T-code creation process?
4.
Auth objects used for table access.
5.
Monthly activities to perform in system
6.
Difference between S_PROGRAM and S_DEVELOP
7.
Critical Auth object in security? S_ADMIN_FCD (Spool admin), S_DATASET (OS file)
S_DEVELOP (Debug access), S_USER_GRP, S_USER_AUTH, S_USER_PRO
8.
Background job auth objects? S_BTCH_ADM, S_BTCH_NAM, S_BTCH_JOB
9.
how to delete a role?
10.
Difference between Data/Enabler role vs Task Role?
11.
Imp tables for derived, composite and single roles?
12.
What happen if we transport role along with user assignment? If user exist/not exist in receiver
13.
What is difference between composite role and business Role
14.
What are the audit activities u know
15.
How to find user email id in ECC
16.
What are diff types of licenses SAP Grant
17.
What is diff between user group in address and group tab in SU01?
18.
What is diff in SUIM for searching T-code in Transaction and Auth object using S_Tcode?
19.
What is the use of personalization tab
20.
What is diff between role and profile
21.
What are different colour code in PFCG
22.
diff modes of PFCG? - when they used
23.
Diff type of Org fields in SAP
24.
t-code to create custom T-code? - SE93
25.
T-code to Transport? and how transport works in SAP? Data Files and Co-files
26.
Type of Transport request? - Custom, Workbench, TOC
GRC1.
Critical action vs critical permission
2.
What is risk? And its type
3.
Diff stages of MSMP? And how it flows
4.
Where to keep the notification mgs? Se61
5.
What are fields present in end user personalization?
6.
What are diff types of GRC Sync jobs
7.
Max number of functions for a risk in GRC?5
8.
How to make/process for custom risk in GRC?
9.
What is diff between centralize and decentralize FFID
10.
Advantage and disadvantage of types of FFID
11.
How to make sure if user is not login with FFID in plugin system
12.
What is Remediation and Mitigation
13.
How to set the mitigation controller/ID? assign to Risk
14.
What are FFowner, FF controller, FFusers
15.
What are diff FF Parameter
16.
What is diff between FF id based and Role based
17. SOD Examples
VA01-creation of sale order vs VF01 - approving sales order
PA30- HR master data vs PA03 - Payroll Control Record
FB60- posting vendor invoice vs FK02 (Vendor master data)
Miscellaneous-http://basisandsecurity.blogspot.com/2015/07/sap-security-interview-questions-and.html
Will Add further on this-